Hair follicle cells
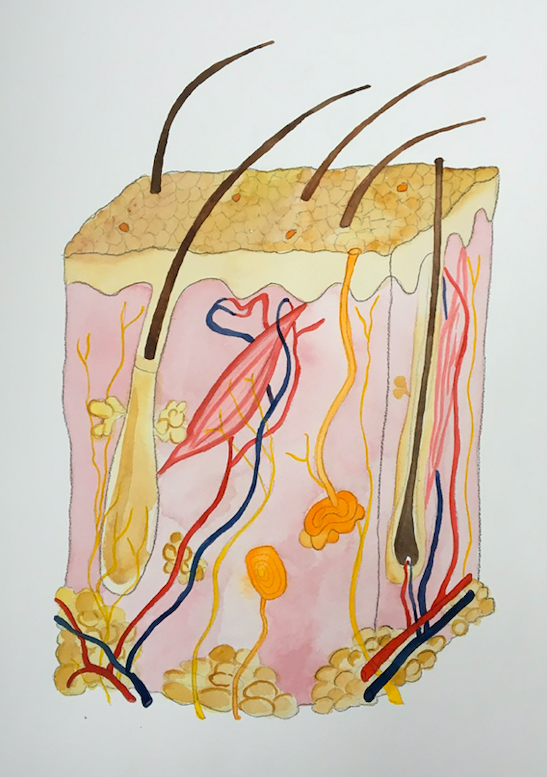
Biorelevant culture of hair follicle stem cells on Biolaminin substrates
Epithelial tissues contain a-5 and a-3 laminin isoforms
Epithelial tissues are a sheet of cells that line the surfaces and cavities of the whole body, including the skin, oral cavity, lung, gastrointestinal and urinary tracts, hair follicles and many glands. The epithelial cells are polarized with the basolateral surface resting on a basement membrane (BM) that contain high levels of alpha-5 laminins and laminin-332. Epithelial BM also contains laminin-311 and to a lesser extent laminin-321 (Domogatskaya, 2012). Laminin-311 forms a covalent complex with laminin-332 in epithelial tissue (Champliaud, 1996) and has been shown to participate in mechanically induced signal transduction after mechanical stimulation (Jones, 2005).
Laminin-332 and laminin-511 constitutes the hair follicle stem cell niche
Laminin-332 and laminin-511 are the major constituents of the BM of the hair follicle (Morgner, 2015). The laminin-332 expression is higher in the interfollicular epidermis (IFE) compared with the deeper portions of the hair follicle. Laminin-511 is less abundant beneath the IFE but with the strongest expression at the isthmus region and around the hair germ (Morgner, 2015), essential for hair follicle down growth (Gao, 2008). Dermal papilla from laminin-511 mutants shows developmental defects (Gao, 2008). Laminin-511 is the primary laminin of the early developing hair. The absence of laminin-511 in transgenic mice leads to a number of developmental abnormalities, including the arrest of hair development and deficient Shh expression in hair follicles (Li, 2003). Skin grafts from Lama5-null mouse embryos grafted onto healthy mice fail to grow hair whereas purified laminin-511 restores hair development in the Lama5-null skin (Li, 2003). In humans and in mice, the absence of laminin-332 results in extensive skin blistering and lethality a few days after birth, highlighting its importance for epidermal architecture (Morgner, 2015).
The ratio between laminin-332 and -511 regulate hair follicle bulge stem cells activation
The hair growth cycle involves three stages: the growth phase (anagen), the regression phase (catagen) and the quiescent phase (telogen). During each anagen phase, follicles are dividing rapidly, adding to the hair shaft. During the catagen and telogen phase, follicles reset and prepare their stem cells so that they can receive a signal to start the next growth phase. Hair loss occurs when the balance between those stages changes. Laminin-511 is upregulated in the anagen phase and exogenous laminin-521 and laminin-511 make adult human hair follicles grow faster (Sugawara, 2007). Laminin-511 is downregulated during the anagen-to-catagen transition, and this downregulation is required for catagen progression. In contrast, Laminin-332 is upregulated in the catagen and antagonized hair growth induced by laminin-511 (Sugawara, 2007). The integrin receptor subunit β1 is central for the maintenance of the quiescent bulge stem cell pool (Morgner, 2015). Inhibition of the β1 integrin disrupted dermal papilla primary cilia formation and hair development (DeRouen, 2010).
Laminin-511 promotes Tgf-β signaling which makes hair follicle stem cells (HFSC) more receptive for activating signals. Contrary, laminin-332 suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling that is required for HFSC differentiation. The ratio between the two laminin isoforms regulates key signaling pathways that determine somatic stem cell activation within the bulge niche (Morgner, 2015).
Exogenous laminin-511 enhances the growth of hair follicle stem cells, whereas the addition of laminin-332 antagonizes this effect. FACS-purified hair follicle stem cells attach very well to laminin-511 coated plates with about 6 times higher well area coverage compared to other cell culture matrices, such as collagen I, fibronectin or Matrigel (Lay, 2016).
Succeed with your application
-
Instructions 001: Coating with Biolaminin substrates
Protocol and concentration calculations for coating cultureware with Biolaminin
Open pdf -
FOXC1 maintains the hair follicle stem cell niche and governs stem cell quiescence to preserve long-term tissue-regenerating potential
Lay K., Kumeb T., Fuchsa E.PNAS, 2016
Read more
Biolaminin Key Advantages
Laminin-332 and laminin-511 are major constituents of the hair follicle microenvironment. Laminin-511 is upregulated in the anagen phase and exogenous laminin-521 and laminin-511 make adult human hair follicles grow faster.
Specific laminin isoforms are present in different tissue microenvironments and are essential for cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Biolaminin products allow you to imitate the natural cell-matrix interactions in vitro.
Our products have consistent composition and quality. This enables minimized variability between experiments and uniform pluripotency gene expression profiles between different cell lines.
All our matrices are chemically defined and animal origin-free, which makes them ideal substrates for each level of the scientific process – from basic research to clinical applications.
Numerous scientists have found our products and finally succeeded in their specific stem cell application. The power of full-length laminins incorporated into various cell systems is well documented in scientific articles and clinical trials.
Recommended products
-

Biolaminin 332 LN (LN332)
Human recombinant laminin 332
Biolaminin 332 supports cells in epithelial basement membranes, lining surfaces of the body such as the skin, hair follicles, oral cavity, gastrointestinal and urinary tract, lungs, and different glands.View product -

Biolaminin 521 LN (LN521)
Human recombinant laminin 521
Biolaminin 521 LN is the natural laminin for pluripotent stem cells and therefore reliably facilitates self-renewal of human ES and iPS cells in a chemically defined, feeder-free and animal origin-free stem cell culture system. LN521 is animal origin-free to the primary level.View product -

Biolaminin 511 LN (LN511)
Human recombinant laminin 511
Biolaminin 511 is the natural laminin for mouse embryonic stem cells and allows sustained pluripotency without the need to use feeder cells or differentiation inhibitors like LIF.View product -

Biosilk
3D culture substrate
Biosilk is a natural biomaterial made of recombinant spider silk protein, a useful tool for a wide range of 3D culture applications, such as organoid culture and other tissue engineering applications. Biosilk can be mixed with any Biolaminin matrix.View product
Talk to our team for customized support
We are here to help you in your journey.