Our technology
A biorelevant cell culture system for robust expansion, maintenance, and subsequent differentiation of human primary cell lines.

Biolaminin key advantages
Full-length laminins are essential for cells in the body; therefore, they make a real difference in the cell functionality of ex vivo cell cultures. Biolaminin products offer a biologically relevant matrix that mimics the authentic ECM-cell interaction.
Biolaminin products are fully defined and batch-to-batch consistent enabling reproducible results and credible conclusions. The products give uniform pluripotency gene expression patterns between cell lines and reduce experimental variability.
Switching to biorelevant Biolaminin in your cell culture system results in more efficient differentiation, cell maturation, and organization of specialized cell types, such as hepatocytes, cardiomyocytes, and neurons.
Biolaminin products are scientifically proven to increase cell proliferation rate with stable phenotype and facilitate the use of low passage cell lines for the production of clinically relevant cell numbers of differentiated cell types.
The products are defined and xeno-free, making them ideal components for basic research and all the way to clinical applications (Cell Therapy Grade). Certificate of Analysis, Animal Origin Free statement, and Material Safety Data Sheet are available for all our products.
Biolamina matrices enable scientific progress
Whether for disease modeling or preparing cells for clinical use, you need a cell culture system that mimics the in vivo environment to achieve high-quality cell products. This is where biorelevant, full-length Biolaminin® proteins come into play. Laminins are important extracellular matrix proteins that surround cells in the body. The effectiveness of the Biolaminin isoforms has been shown in a multitude of publications: take a look at these scientific innovations by our customers.
-
Publication: Single-cell transcriptomics captures features of human midbrain development and dopamine neuron diversity in brain organoids
Fiorenzano et al. 2021 Nature Communications
 Read more
Read more
-
Generation of high-purity human ventral midbrain dopaminergic progenitors for in vitro maturation and intracerebral transplantation
Nolbrant S., Heuer A., Parmar M., Kirkeby A. Nature Protocols, 2017
 Read more
Read more
-
Protocol for automated production of human stem cell derived liver spheres
Jose Meseguer-Ripolles, Alvile Kasarinaite, Baltasar Lucendo-Villarin, David C Hay. STAR Protoc, 2021
 Read more
Read more
-
Monolayer culturing and cloning of human pluripotent stem cells on laminin-521 based matrices under xeno-free and chemically defined conditions
Rodin S., Antonsson L., Hovatta O., Tryggvason K. Nature Protocols, 2014
 Read more
Read more
Laminin Biology
Laminins are key proteins in the basement membrane
Laminins are a large family (at least 16 different isoforms expressed in mammals) of conserved, multidomain glycoproteins comprising the extracellular matrix. They are a major component of the basal lamina, a protein network that is the foundation for most cells and tissues. Laminins have an important biologically active role and are vital for the maintenance and survival of tissues and, importantly, most laminins exhibit high cell-type specificity. Without the right combination of laminin isoforms, cells and tissues become dysfunctional.
Each laminin isoform consists of three inter-coiled chains -an α, β, and γ chain – that exist in five, four, and three genetically distinct variants, respectively. The laminin isoforms are named according to their chain composition. For example, a combination of an α5 chain, a β2 chain, and a γ1 chain, forms laminin 5-2-1 (LN521). The trimeric proteins form a cross-like structure that can bind to other extracellular matrix molecules and various cell membrane receptors.
Tissue-specific culture substrates for improved cell functionality
In the body, cells reside in highly specialized, chemo-and mechanosensitive microenvironments, or “niches”, which serve to protect and maintain the cells and to respond to the needs of the surrounding tissue. α5 chain laminins (511 and 521) are the key cell adhesion proteins of the natural Laminin expression in the blastocyst stem cell niche, expressed and secreted by the embryonic stem cells of the embryo’s inner cell mass. The Biolaminin 521 cell culture substrate thus recapitulates the most biologically relevant milieu for hESCs and iPSCs cultured in vitro and is a critical autocrine and paracrine factor for regulating survival and self-renewal. Tissue-specific laminin isoforms can also be used for robust differentiation of specialized cell types, such as hepatocytes, skeletal muscle cells, and various neural cells.
Each laminin isoform consists of three inter-coiled chains -an α, β, and γ chain – that exist in five, four, and three genetically distinct variants, respectively. The laminin isoforms are named according to their chain composition. For example, a combination of an α5 chain, a β2 chain, and a γ1 chain, forms laminin 5-2-1 (LN521). The trimeric proteins form a cross-like structure that can bind to other extracellular matrix molecules and various cell membrane receptors.
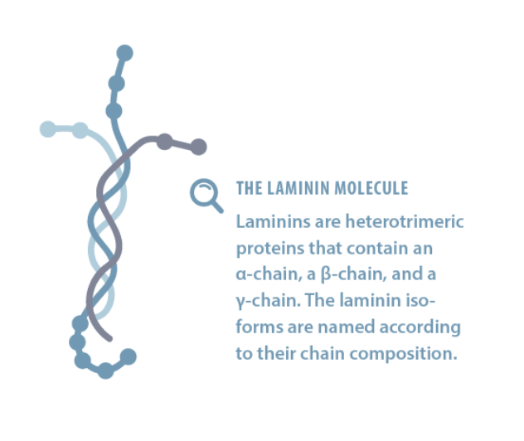
Only the intact, full-length laminin molecules can replicate the biologically relevant conditions
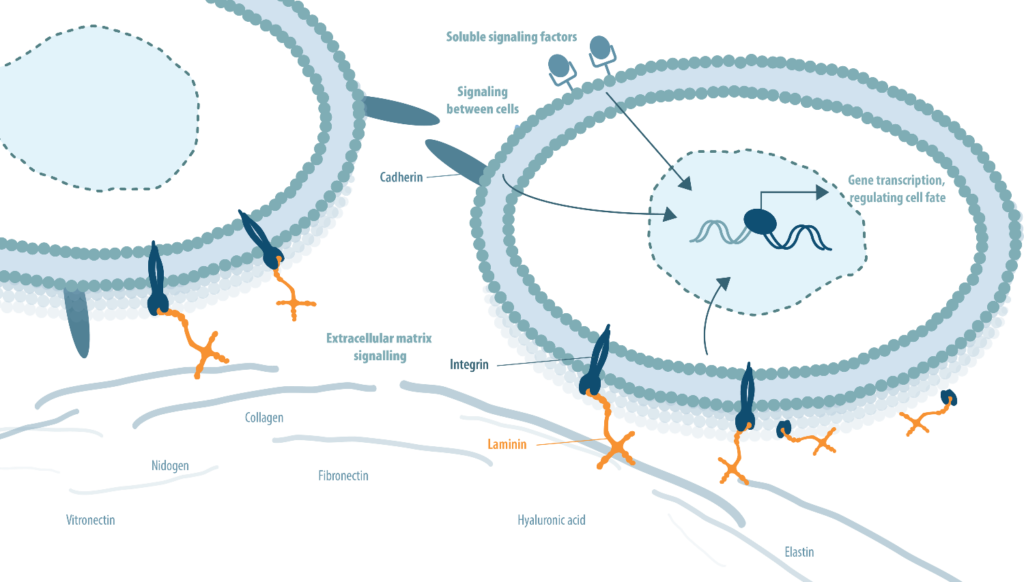
There are many binding motifs on the full-length laminin molecule that can interact with cell membrane receptors. It has been suggested that the molecular mechanism underlying the laminin-mediated signaling involves the C-terminal region of laminins but integrins and other cellular receptors also interact with some of the N-terminal globular domains. Laminins are also capable of co-signaling with growth factors and efficiently buffer endogenously produced growth factors, thereby adding to the mechanistic complexity. Via binding to specific cellular receptors, laminins regulate cellular responses, such as cell anchorage, survival, proliferation, migration, organization and specialization, leading to improved cell functionality.
The crucial extracellular microenvironment
Stem cells are influenced by the coordinated interaction of soluble factors, extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, and signals from neighboring cells. This multifaceted cell-ECM communication takes place through both integrin and non-integrin membrane-bound receptors and induces complex intracellular signaling pathways with subsequent effects on survival, self-renewal, migration, morphogenesis, and differentiation.
Full-length laminins for authentic cell culture from basic research to clinical applications
BioLamina offers an expansive portfolio of defined, animal origin-free, recombinant laminin cell culture substrates, Biolaminin®, for a variety of applications in 2D and 3D, including reliable expansion of human pluripotent stem cells (hESC and iPSC) and differentiation and maintenance of different specialized cell types, such as hepatocytes, pancreatic cells, and various neural cells. The Biolaminin substrates allow you to imitate the natural cell-matrix interactions in vitro. The authentic cell culture environment gives more consistent and reliable cellular responses and improves cell functionality. Biolaminin substrates are the only original full-length, recombinant laminins on the market. A fragmented or truncated laminin molecule or laminins isolated from tissue lack many of the laminin domains that cells need for the proper extracellular network to form and to stimulate correct cellular signal transductions. Hence, only the intact, full-length laminins can create a more authentic cell culture environment.
Our range of Biolaminin matrices is tailored to take you from reproducible research to cell therapy development. They are defined, animal origin free, and documented to comply even with strict regulatory requirements. The beneficial effects of our products for primary cell culture will help you scale up cell production and enhance your cell models.
- Biolaminin LN is animal origin-free to the primary level
- Biolaminin MX is animal origin-free to the secondary level
- Biolaminin CTG is animal origin-free to the secondary level and designed for clinical studies
Learn more about laminins
-
Other10/06/2021
Quality documents
Quality documents Quality certifications ISO 9001 certificate Safety data sheets Biosilk (BS)Biosilk
-
Other01/06/2021
Videos: Introduction to laminins
Introduction to laminins Stem cell culture on Biolaminin 521 Stem cell culturing is easy on human re
-
Developing defined substrates for stem cell culture and differentiation
Hagbard L.,bCameron K., August P., Penton C., Parmar M., Hay D.C., Kallur T.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B, 2018
Read more -
Molecular Basis of Laminin–Integrin Interactions
Yamada M. and Sekiguchi K. Current Topics in Membranes, 2015
Read more -
Functional diversity of laminins
Domogatskaya A., Rodin S., Tryggvason K. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 2012
Read more -
Infographics: Biolaminin 521 cell culture substrates
See how our CT, and MX products differ
Open pdf -
Application overview 008: Full-length laminin proteins are crucial for stem cells
Full-length laminins are crucial components in creating the stem cell niche in vivo and in vitro
Open pdf
WHAT OUR CUSTOMERS SAY
“We struggled for a number of years to establish a GMP manufacturing process for generating DA neurons from human embryonic stem cells in order to develop a stem cell-based therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. The recombinant laminins from BioLamina really made a world of difference! We now routinely use LN521 and EDTA for passaging the pluripotent stem cells and we have greater efficiency than ever before.”

Prof. Malin Parmar,
Lund University, Sweden
Introducing Biosilk™: a defined biomaterial for 3D primary cell culture and organoid formation

Talk to our team for customized support
We are here to help you in your journey.