The dancing full-length laminin in higher resolution
While advanced microscopy techniques have previously facilitated the imaging of cross-shaped laminin proteins, these methods were limited to capturing snapshots of individual conformational states or producing low-resolution dynamic images lacking submolecular details.
This study reported an optimized method for studying the dynamic motion of full-length laminin protein under physiological conditions using high-speed atomic force microscopy.
The cell adhesion domain of the examined Biolaminin protein isoforms displayed structural dynamism, alternating between open and compact conformations. This suggests that the cell-binding interface could be more dynamic than previously thought, potentially influencing adhesion receptor binding.
Full-length laminin as the innate cell culture matrix
As a multi-adapter protein, laminin functions as a bridge connecting cells to the extracellular matrix network, transiting signals into the cell.
Laminin is not a static molecule but moves dynamically along the entire full-length configuration, influencing cell survival and identity.
Dynamic movements of full-length laminin protein were observed using high-speed atomic force microscopy. (Akter et al. 2024, video S4, CC BY 4.0)
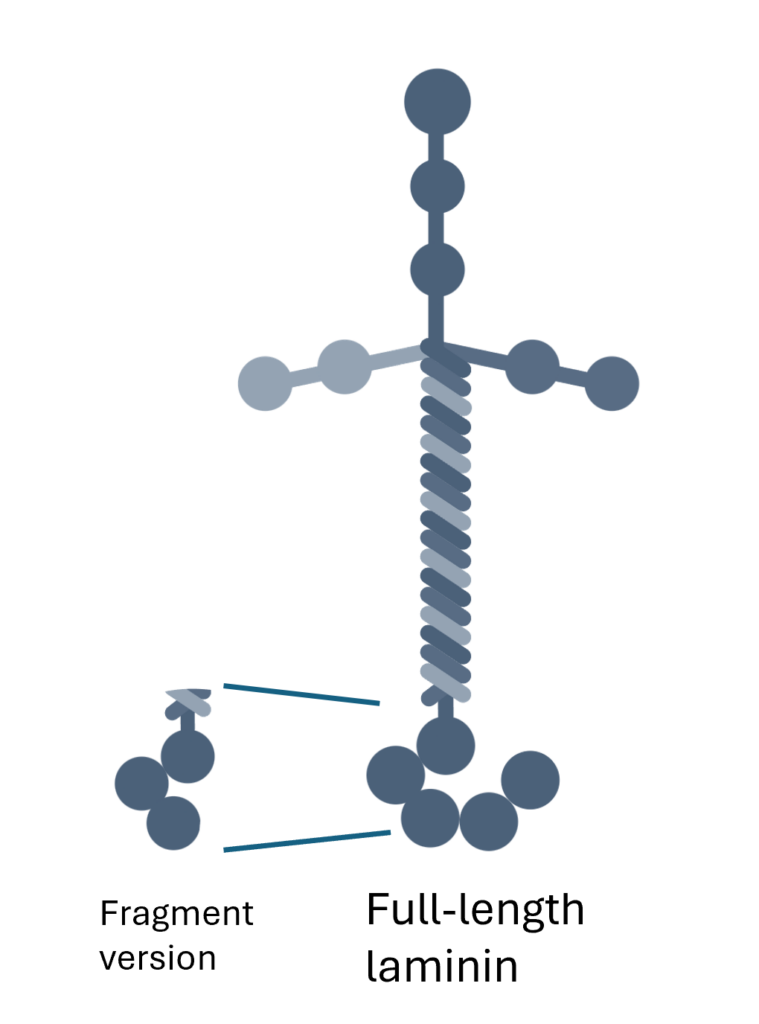
Unlike fragmented products, the only full-length laminin product, Biolaminin®, provides cells with comprehensive in vivo signaling in vitro.
Talk to our team for customized support
We are here to help you in your journey.